General Surgeries / Hernia / Laparoscopic
Hernia: Everything that you need to know

by admin
27th April 2021
10 minutes read
Experiencing a painful protrusion near your chest, abdomen, or genitals? It could be a sign of a hernia. You’re not alone. Hernias are a common medical condition in India, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. They can occur in various forms, including inguinal hernias, umbilical hernias, hiatal hernias, and more. The prevalence of hernias in India is attributed to factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices, and physical labor.
In this comprehensive guide curated by Medfin experts, we cover all major aspects like – the symptoms, the primary factors that trigger it, treatment options, and much more.
So, without further ado, let’s dive into our first segment.
What is Hernia?
A hernia is a medical condition where an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue, causing a bulge or lump. This can lead to pain, discomfort, and potentially serious complications. Hernias commonly occur in the abdominal wall. Treatment options include hernia surgery, such as hernioplasty or herniorrhaphy, to repair the weakened area and return the protruding organ or tissue to its proper place. Hernia treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the patient’s quality of life through surgical or non-surgical interventions.
Signs and Symptoms You Must Look Out For
A Visible Bulge: You will notice a lump or bulge in the area. It is more prominent while you stand up and while straining or coughing.
Pain: Hernias may result in a sharp, aching pain that can aggravate during certain activities such as lifting heavy weights.
Heart Burn: Some hernias may cause can cause heartburn, acid reflux, or a burning sensation in the throat.
Nausea and Vomiting: Severe cases of hernia can cause bowel obstruction leading to nausea, vomiting, or constipation.
Change in Bowel Habits: Hernias may also disrupt normal bowel movements and may cause constipation or diarrhea.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you must immediately consult a professional as any delay in treatment can result in unwanted complications
Causes of Hernia
Hernias typically result from a combination of muscle weakness and increased pressure on the affected area. Common causes and risk factors for hernias include:
- Congenital muscle weakness
- Aging
- Heavy Lifting
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Chronic Cough
- Straining during bowel movements
- Previous surgery
- Family history of hernias
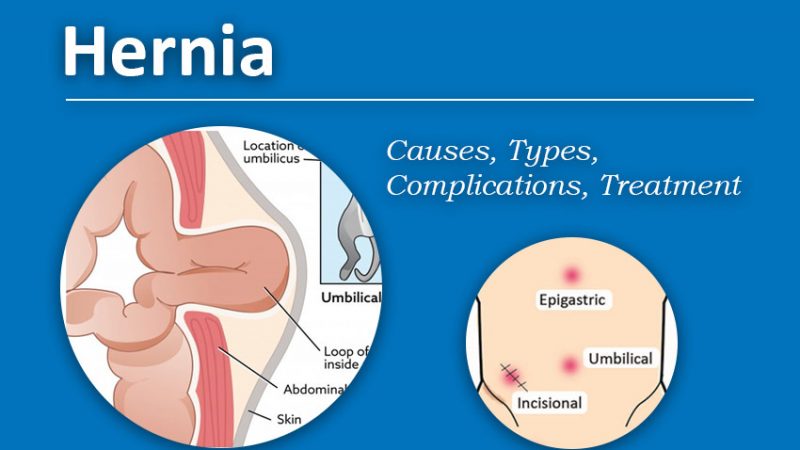
Different Types of Hernia
Some of the common types of hernia are listed below
- Inguinal Hernia: This is the most common type of hernia and occurs in the groin area. It can be further categorized as direct (through a weak spot in the abdominal wall) or indirect (through the inguinal canal).
2. Femoral Hernia: Less common than inguinal hernias, femoral hernias appear in the upper thigh or groin and are more common in women.
3. Umbilical Hernia: These hernias develop around the navel or belly button and are often seen in infants, pregnant women, or obese individuals.
4. Incisional Hernia: These occur at the site of a previous abdominal surgery or incision, where the abdominal wall may have weakened.
5. Hiatal Hernia: Found in the upper stomach area, a hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, often leading to acid reflux symptoms.
Epigastric Hernia: These hernias occur between the breastbone and the navel and involve fatty tissue pushing through the abdominal wall.
Each type of hernia may present with specific symptoms and require different treatment approaches, which can range from watchful waiting to surgical repair. It is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.
Diagnosis & Treatment Options
Hernias are typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging studies. Once a hernia is diagnosed, your healthcare provider will discuss treatment for hernia and recommendations based on the type and severity of the hernia.
Hernia treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the hernia. Common treatments include:
Watchful Waiting:
For small, asymptomatic hernias, your healthcare provider may recommend monitoring without immediate intervention. Lifestyle modifications such as weight management and avoiding heavy lifting may be advised.
Hernia Surgery (Herniorrhaphy or Hernioplasty):
Surgical repair is often recommended for larger or symptomatic hernias. Herniorrhaphy involves sewing the hernia opening closed, while hernioplasty uses a mesh to reinforce the weakened area. These procedures can be performed using open or minimally invasive techniques.
Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery:
A minimally invasive approach involving smaller incisions, reduced pain, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery. It is commonly used for inguinal and umbilical hernias.
Home Remedies:
Some individuals may seek hernia relief at home through methods like wearing a supportive belt or truss. However, these are not long-term solutions and should be used under a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding straining during bowel movements, and managing conditions like chronic cough or constipation can help prevent hernias from worsening.
The choice of treatment depends on factors like the type and size of the hernia, symptoms, patient health, and surgeon recommendations.
Complications of Hernia
Hernias can lead to various complications, some of which can be serious and require immediate medical attention. Common complications include:
Strangulation:
This is a critical complication where a portion of the herniated tissue becomes trapped and loses its blood supply. It can lead to severe pain, tissue damage, and necrosis (tissue death). Strangulated hernias require emergency surgery.
Obstruction:
Hernias can cause a partial or complete blockage of the bowel, leading to symptoms like severe abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, and an inability to pass gas or stools. Bowel obstruction is a medical emergency and requires prompt treatment.
Incarceration:
In this complication, the hernia cannot be pushed back into the abdominal cavity and becomes trapped outside the abdominal wall. While not as severe as strangulation, it still requires surgical repair.
Perforation:
In rare cases, hernias can cause a tear or perforation in the intestine, allowing the contents to leak into the abdominal cavity. This can lead to peritonitis, a life-threatening infection of the abdominal lining.
Chronic Pain:
Some individuals may experience persistent pain at the hernia site, even after surgical repair. This is known as chronic post-herniorrhaphy pain syndrome (CPHPS) and can be challenging to manage.
Preventive measures and early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing hernias and reducing the risk of complications.
Hernia: Preventive Measures
The following measures can help lower the risk of hernias
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Use proper lifting techniques while lifting heavy weights.
- Have a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and straining while passing stools.
- Quit smoking as it increases the risk of developing hernias.
- Manage conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in order to prevent chronic cough.
- Maintain a good posture in order to avoid unwanted strain on the abdominal muscles.
Remember that while these preventive measures can reduce the risk of hernias, they may not eliminate the possibility entirely.
What Triggers It?
There are different kinds of hernia causes that we must keep an eye out for. Some of the most common causes include:
- Weakened muscles
- Aging
- Repeated strain on the groin and abdominal region
- Obesity
- Heavy lifting
- Long-lasting heavy cough
- Weakening of diaphragm with age/pressure
- Excess gastritis
You will get a clear insight into the causes once you’ve gone through our Types of Hernia section.
Different Types in Men and Women
According to experts, multiple types exist in the medical field. Some of the most common types are listed below:
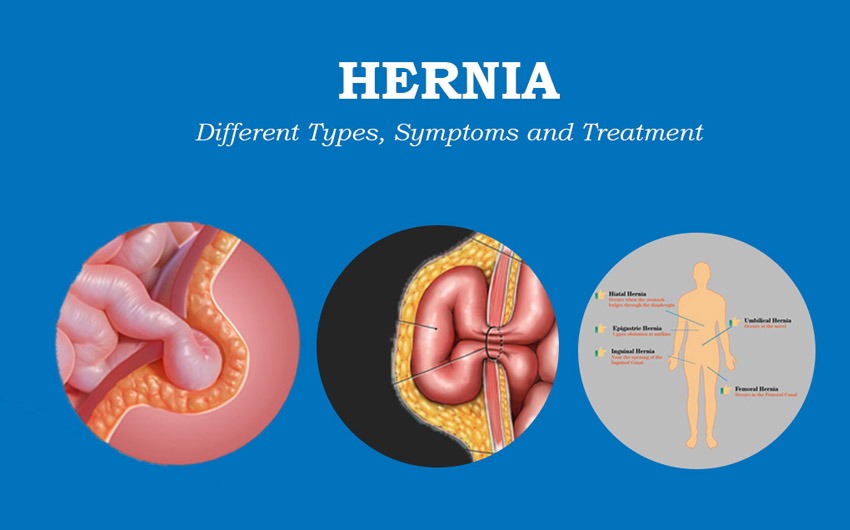
1. Inguinal Hernia
It occurs when tissue pushes through a weak spot in the groin muscle and is commonly found in men.
2. Femoral Hernia
It occurs when the tissue bulges from the lower belly into the upper thigh, just below the groin crease. You may experience pain in the groin area and hence is often mistaken for an inguinal one.
3. Umbilical Hernia
It occurs when intestines, fat, or fluid pushes through a weak spot in your belly. If you’re suffering from this type, you may notice a bulge near the belly button or navel.
4.Hiatal Hernia
It’s different from other hernia types because, in this type, your stomach starts bulging through the diaphragm and into your chest.
According to reports, an inguinal one is the most common type making up to nearly 75% – 80% of cases around the world.
Diagnosis & Treatment Options
Before initiating any treatment, medical experts conduct your physical examination to determine which type affects your body. They analyze your complete medical history to see if any medical condition is the deciding factor triggering this disease.
If your hernia shows negligible symptoms, the doctors prefer waiting and monitor your condition consistently. However, it can be fatal if you’re suffering from the femoral type of hernias.
In the else case, when your hernia does show a certain symptom, the following treatment options are undertaken:
1. Open surgery
A cut is made on your body at the location of the disease, and the tissue is set back in place, while the weakened muscle is stitched back.
2. Laparoscopic surgery
To conduct this hernia surgery, doctors make tiny incisions on your body instead of cutting outside the groin/abdomen regions. The tiny incisions are large enough to allow surgical tools to penetrate within your body and complete the hernia laparoscopic surgery procedure.
Before finalizing any treatment option, you must discuss the pros and cons of each surgery method and the average hernia surgery cost with your doctor and then make a final decision.
Does it Have Any Complications?
As per doctors, the common complications associated with the surgery are:
1. Seroma
A collection of white fluid in the wound
2. Mesh infection
It’s the most dangerous complication of hernia diseases. It requires removal of mesh thorough cleaning of the wound and culture-based antibiotics
3. Pain
Which may subside by consuming common painkillers
4. Hematoma
A collection of blood in the wound
To avoid recurrence, you must avoid putting too much pressure on sensitive regions like the abdomen or groin. It’s best to consult a certified professional to learn about the different hernia reasons and the best ways to administer the treatment.
FAQs on Hernia: All Your Queries Answered
Yes, a hernia can be painful in most cases. There’s no particular duration of how long a hernia can last. However, according to experts, you must seek medical advice at the first instance of hernia symptoms. Post-treatment, you must adhere to the precautions to avoid recurrence and prevent discomfort.
No, there’s no age bar for getting a hernia. Children and adults of all age groups can suffer from hernia depending on the level of physical activity like weight lifting, stress, etc., and various other factors.
It depends on the type and severity of the hernia and should be discussed with a healthcare provider. In some cases, low-impact exercises and physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the surrounding muscles and help manage symptoms. However, high-intensity or heavy lifting exercises should be avoided, as they can exacerbate hernia symptoms and increase the risk of complications.
In general, hernias do not heal on their own. Once a hernia has developed, it tends to persist and often worsen over time. Without medical intervention, hernias are unlikely to resolve by themselves. Surgical repair is usually required to fix the herniated tissue and strengthen the weakened abdominal wall.
CATEGORIES
- ACL Reconstruction
- Anal Fissures
- Anal Fistula
- Appendicitis
- ASK A DOCTOR
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Breast Lump Excision
- Cataract
- Circumcision
- Conditions & Diseases
- Cosmetology
- Covid-19
- Cure
- Endocrinology
- ENGLISH VIDEOS
- Eye Care
- Gallstones
- General Surgeries
- Government Schemes
- Gynaecology
- Gynecomastia
- Health
- Health Insurance
- Hernia
- Hindi
- Hip Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- Hip Replacement Surgery
- Hydrocele
- Kannada
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Arthroscopic
- Laparoscopic
- LASER
- Latest Treatments
- Lifestyle
- Liposuction
- Medfin Stories
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedic
- Paraphimosis
- Patient Testimonials
- PCL Reconstruction
- Phimosis
- Piles (Hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Sinus
- Proctology
- Prostate Artery Embolization
- Rhinoplasty
- Second Opinion
- Total Knee Replacement
- Urology
- Uterine Artery Embolization
- Uterine Fibroids
- Varicocele
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular
- VIDEOS